Baclofen
Baclofen is a skeletal muscle relaxant, which is used in the treatment of muscle spasticity. The brand name of baclofen is, Lioresal. It is an antispasmodic drug. Baclofen is a monocarboxylic acid derivative, an odorless, white crystalline powder. Baclofen is slightly soluble in water. The molecular weight of baclofen is 213.6 gm/mol. Baclofen is used in the treatment of hiccups.
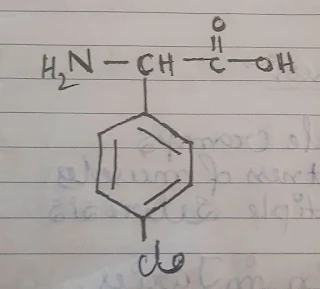
Structure:
The molecular formula of baclofen is, [C10H12NO2Cl].
The IUPAC name of baclofen is 4-amino-3-(4-chlorophenyl)butanoic acid.
Synthesis:
Mechanism of action:
The exact mechanism of action of baclofen is unknown. It is a GABA(Gamma Amino Butyric Acid) agonist. It's bound with GABA receptors and decreased the calcium influx at the presynaptic nerve terminal. Due to this baclofen reduced the release of the excitatory neurotransmitters in the pre-synaptic neuron and inhibit the inhibitory neural signals in post-synaptic neurons. Due to this spasticity is reduced.
Uses:
It is used in the treatment of,
- Muscle cramps.
- Tightness of muscle.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Spine injuries.
- Hiccups
Side-effects:
the overdose shows different types of side effects like,
- Weakness.
- Nausea.
- Confusion.
- Tiredness.Dizziness.
- Staying asleep
- Vomiting.


Post a Comment