Mebendazole
Mebendazole is an anthelmintic agent used in the treatment of parasite worm infection. It is a white to off-white powder. Mebendazole is insoluble in ethanol, water, chloroform, etc. It is a benzimidazole derivative. The molecular weight of mebendazole is 295.2 gm/mol. It is also known as, Mebuter, Vermicidin, Telmin, Vermox, Pantelmin, Noverme, Mebendazolum, Verpanyl, Ovitel, etc.
Structure:-
The molecular formula of mebendazole is,[C16H13N3O3].
The IUPAC name of mebendazole is, methyl-N-(6-benzoyl-1H-benzimidazole-2-yl) carbamate.
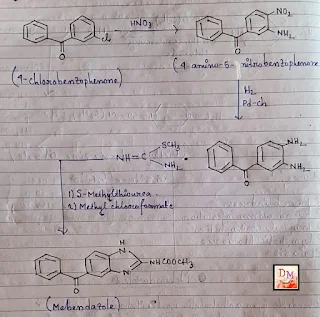
Synthesis:-
Mechanism of action:-
It inhibits tubulin polymerization into cytoplasmic microtubules by binding to the colchicine-sensitive site of tubulin. These microtubules are required for glucose uptake in the larval and adult stages of the parasite. due to the inhibition, the amount of glycogen is reduced in parasite body. So the production of ATP is decreased and the parasite is dead.
Uses:-
It is used in the treatment of several worm infections like,
1. Roundworm infection. (Ascariasis)
2. Hookworm infections. (Uncinariasis)
3. Tapeworm infection.
4. Threadworm infection.
5. Guinea worm infection.
6. Whipworm infection.
Side-effects:-
The overdose of mebendazole shows the different type of side-effect like,
- Hives.
- Skin rash.
- Itching.
- Fever.
- Abdominal pain.
- Convulsions.
- Black, tarry stools.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Diarrhea and Headache.


Post a Comment