Dibucaine
Dibucaine is a amine derivative local anesthetic. It is a solid, colorless and almost colorless powder. Dibucaine is odorless. The melting point of dibucaine is 99-101⁰c (HCl salt). Dibucaine is insoluble in water, Soluble in ethanol, chloroform ether, petroleum ether, acetone. The molecular weight of dibucan is, 343.5 gm/mol. The pKa value of dibucaine is 8.85. It is sensitive to light. It is also known as, Cincocainio, Sovcaine, Percamine, Dibucainum, Nupercainal etc.
Structure-
The moleculer formula of dibucaine is, [C20H29N3O2].
The IUPAC name of dibucaine is, 2-butoxy-N-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]quinoline-4-carboxamide.
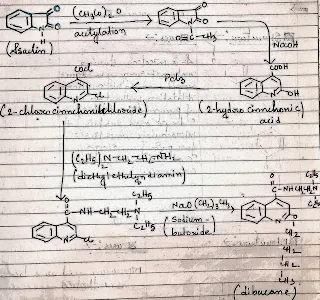
Synthesis-
The starting material of dibucaine synthesis is isaclin.
Mechanism of Action-
It reversibly binds to and inactivate sodium channels in the neuronal cell membren. Inhibition of sodium channels prevents the depolarisation of nerve cell membrens and inhibits subsequent propagation of impulses along the course of the nerve, thereby limiting the excitation of nerve endings.
Uses-
*This medication is used in the skin to stop itching and pain from certain skin conditions (such as scrapes, minor burns, eczema, insect bite).
*It is also used to treat minor discomfort and itching caused by hemorrhoids.
*It is a local anesthetic that works by causing temporary numbness/loss of feeling on the skin.
Side effects-
The overdose of dibucaine shows different types of adverse effect like,
#Skin rash.
#Hives.
#A stining sensation on the skin.
#Angioedema.
#Erythema.
#Itching.
#Skin inflammation due to topically applied medication.


Post a Comment