Acetazolamide
The trade name of Acetazolamide is Diamox. It is a sulfonamide derivative. It appears as white to yellowish-white crystalline powder. Acetazolamide is odorless and tasteless. The molecular weight of Acetazolamide is 222.3. It is sparingly soluble in cold water and slightly soluble in alcohol. It is insoluble in chloroform and diethyl ether. It is also known as, Acetamox, Donmox, Vetamox, Diutazol, Eumicton, Cidamex, Acetazolamida, Acetazolamine, Atenezol, Diacard, Defiltran, Edemox etc
Structure-
The molecular formula of Acetazolamide is, [C4H6N4O3S2].
The IUPAC name of acetazolamide is, N-(5-sulfomyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)acetamide.
Mechanism of action-
Acetazolamide is carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. That means this drug works to cause an accumulation of carbonic acid by preventing its breakdown. The result is lower blood pH, given the increased carbonic acid which has a reversible reaction into bicarbonate and the hydrogen ion.
Carbonic anhydrase is found in red blood cells and the kidney's proximal tubule. It works to reabsorbate sodium, bicarbonate, and chloride. Once Acetazolamide inhibits carbonic anhydrase, sodium, bicarbonate, and chloride get excreted rather than reabsorbed; this also leads to the excretion of excess water. The clinical result is a decrease in blood pressure and intracranial and intraocular pressure.
Bicarbonate excretion also increases the acidity of the blood, aqueous humor level decreases in the eyes, and there are compensatory mechanisms for increased blood acidity, such as hyperventilation.
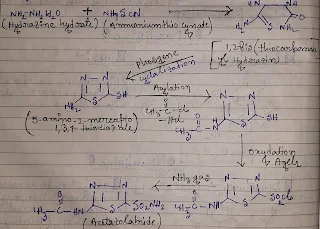
Synthesis-
The starting material of acetazolamide Synthesis is hydrazine hydrate.
Uses-
*This medication is used in glaucoma, a condition in which increased pressure in the eye can lead to gradual loss of vision.
*It is also used in epilepsy, altitude sickness, and periodic paralysis.
Side effects-
There have been reports of central nervous system toxicity with positive symptoms including fatigue, lethargy, and confusion. The common symptoms are,
#Paresthesias.
#Tinnitus.
#Drowsiness.
#Anorexia.
#Altered taste.
#Nausea.
#Vomiting.
#Diarrhea.
#Ployruria.
Symptoms self-resolve after discontinuation of Acetazolamide. There is no specific antidote to an overdose of Acetazolamide.


Nice
ReplyDeletePost a Comment