Sulfacetamide
It is a sulfonamide antibacterial agent and sulfanyl acetamide derivative. It is used in the treatment of urinary tract infections and some skin infections. It is a white powder, which is slightly soluble in water the molecular weight of sulfacetamide is 214.2 gm/mol and the melting point is, 360 to 363°C. It is also known as, Acetocid, Alesten, Albamine, Albusid, Sebizon, Opthel-S, Klaron, Sulfacet, Acetosulfamine, etc.
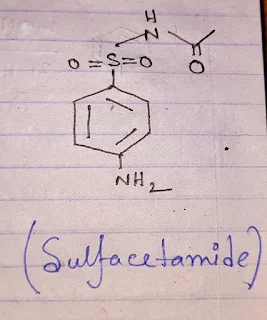
Structure:
The molecular formula of sulfacetamide is,[C8H10N2O3S].
Synthesis:
The reaction between 4-aminobenzene sulphonamide with acetic anhydride and controlled H2O produced Sulfacetamide.
Mechanism of action:
Sulfacetamide reacts with a bacterial folic acid synthesis which is very important for the bacterial organism. It interferes with folic acid synthesis by inhibiting Para-Amino benzoic Acid(PABA), which is necessary for bacterial growth.
Uses:
It is used in the treatment of several infections like Conjunctivitis, Vaginitis, Blepharitis, Keratitis, etc.
Side-effects:
The overdose of sulfacetamide shows different types of adverse effects like,
- Fever.
- Joint pain.
- Sores in the mouth.
- Cracked and dry skin.
- Rash hives.
- Itching.
- Difficulty in breathing.
- yellow skin or eyes.


Post a Comment