Amphetamine
Amphetamine is a CNS stimulant used in the treatment of ADHD( Attention Deficit Hyper Activity Disorder) and narcolepsy. The trade name of amphetamine is Adderall and Mydayis. Amphetamine is a colorless liquid with an amine odor and a burning taste. It is soluble in ethanol, chloroform and slightly soluble in water. The molecular weight of amphetamine is 135.2 gm/mol. It is also known as, Centramina, Actedron, Mecodrin, Benzebar, Adipan, Fenopromin, etc.
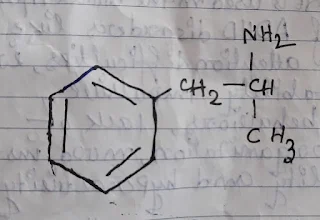
Structure:
The molecular formula of amphetamine is, [C9H13N].
The IUPAC name of amphetamine is, 1-phenylpropan-2-amine.
Synthesis:
Mechanism of action:
Amphetamine is a CNS stimulant, and its effects on dopamine, nor-epinephrine, and serotonin. It releases the catecholamines like noe-epinephrine and dopamine from the pre-synaptic terminal, due to this the reuptake of dopamine, nor-epinephrine, and serotonin is blocked and increases the release of catecholamine in synaptic space.
Uses:
It is used in the treatment of ADHD( Attention Deficit Hyper Activity Disorder) like attention difficulties, impulsive behaviors, lack of organization, mood instability, and hyperactivity. It is also used in the treatment of narcolepsy or "sleep attacks", obesity, and depression.
Side-effects:
The overdose of amphetamine shows different types of side effects like,
- High or low blood pressure.
- Abdominal pain.
- Blurred vision.
- Dry mouth.
- Nasal congestion.
- Acne, rash, hives.
- Weight loss
- nausea
- loss of appetite.
- Teeth grinding, Nosebleed.


Post a Comment