Bromocriptine
Bromocriptine is an antiparkinson drug, which is a semisynthetic dopamine agonist. It is an ergoline derivative(ergot alkaloids). Bromocriptine treats Parkinson's disease, Type2 diabetes, Pituitary tumors, Hyperprolactinaemia, etc. it is a white crystalline solid, which is soluble in ethanol, and DMSO, and slightly soluble in water. The molecular weight of bromocriptine is 654.60 gm/mol.
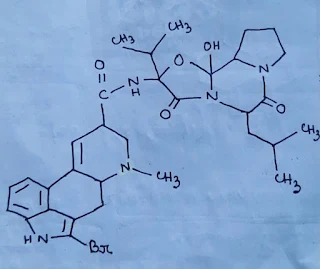
Structure:
The molecular formula of bromocriptine is,[C32H40N5O5Br].
The IUPAC name of bromocriptine is, (5'a)-2-bromo-12'-hydroxy-5'-(2-methylpropyl)-2'-(propan-2-yl)-3',6',18-trioxoergotaman.
Synthesis:
Mechanism of action:
Bromocriptine is a dopamine receptor agonist. It binds with D2 receptors. The D2 receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor. The inhibition of the D2 receptor causes the inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. This adenylyl cyclase is very important in the conversion of cAMP. due to this the protein kinase is decreased. Due to the inhibition of the D2 receptor the intracellular calcium level is increased. This inhibits motor neuron functions and treats Parkinson's disease.
Bromocriptine when binds with the dopamine receptors. it increased dopamine activity. Due to this insulin and glucose production is decreased.
Uses:
It is used in the treatment of,
- Parkinson's Disease.
- Amenorrhea.
- Type2 diabetes.
- Pituitary tumors
Side-effects:
The overdose of bromocriptine shows different types of side effects like,
- Hypotension.
- Abdominal cramps.
- Dizziness.
- Indigestion.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Insomnia.
- Visual hallucination.


Post a Comment